Step by Step SSL Handshake with Wireshark
Let’s look at each and every network packet that passes between client and server during an SSL Handshake. Before any appliction data can flow through, the SSL Handshake between Client and Server needs to be completed. It is similar to an agreement, where both agrees on few standards, based on which, communication is established.
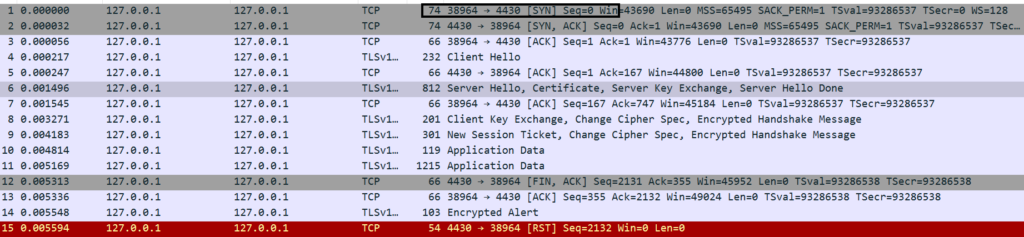
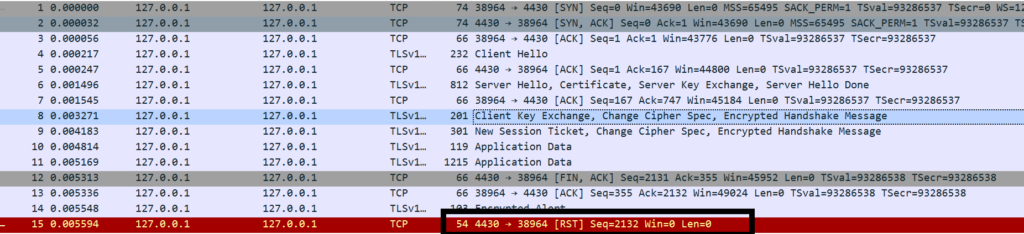
Step1. Client sends SYN packet to server.
Note that in all the below screenshots, both the client and server are residing in local (127.0.0.1). Hence, the source and destination has same IP.
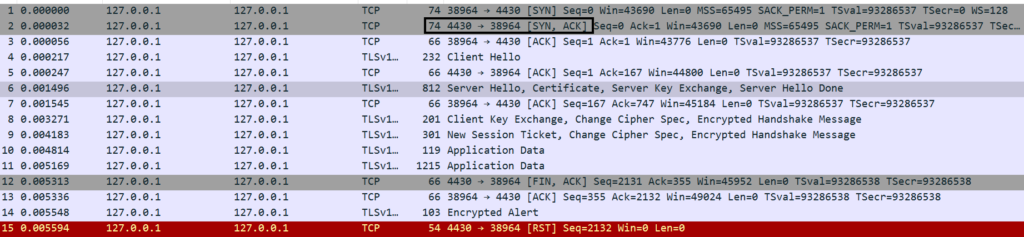
Step2. Server responds with SYN/ACK
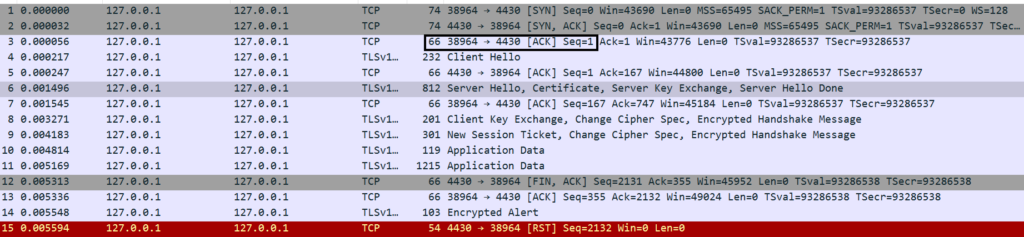
Step3. Client acknowledge with ACK. At this step, the 3-way-TCP-Handshake has completed. Any socket connection has to complete this 3-way-TCP-Handshake. However, note that this is different from the SSL handshake, which has not kicked in yet.
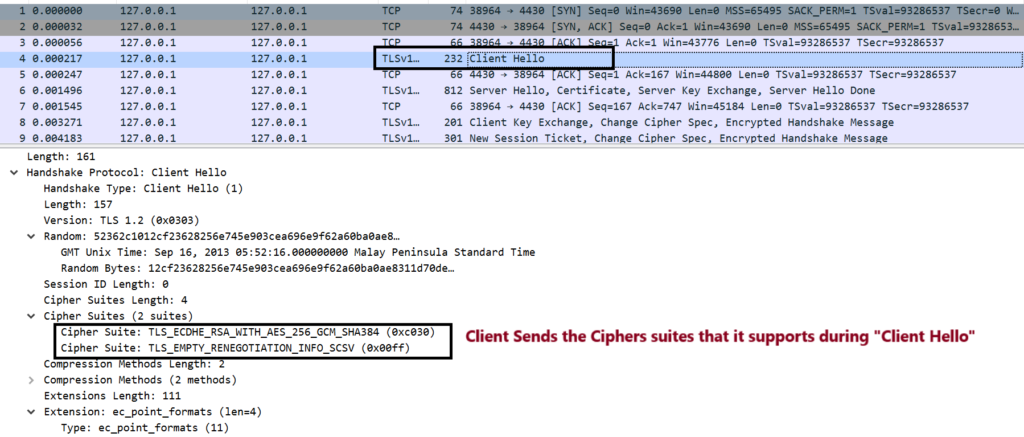
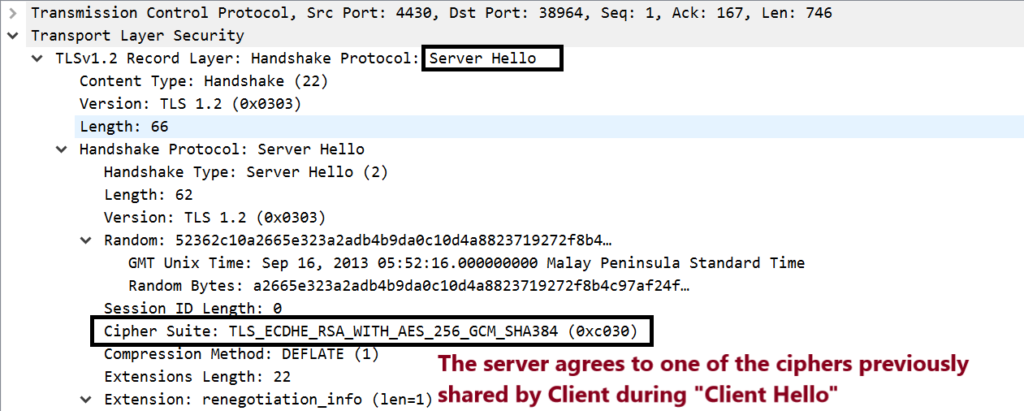
Step4. Now, the steps for SSL Handshake begins. Client sends “Client Hello” to Server. Along with that, it sends the set of Cipher Suites that it supports.
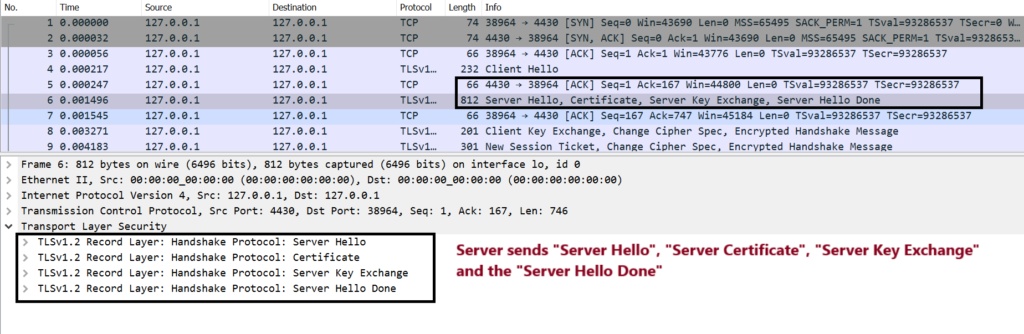
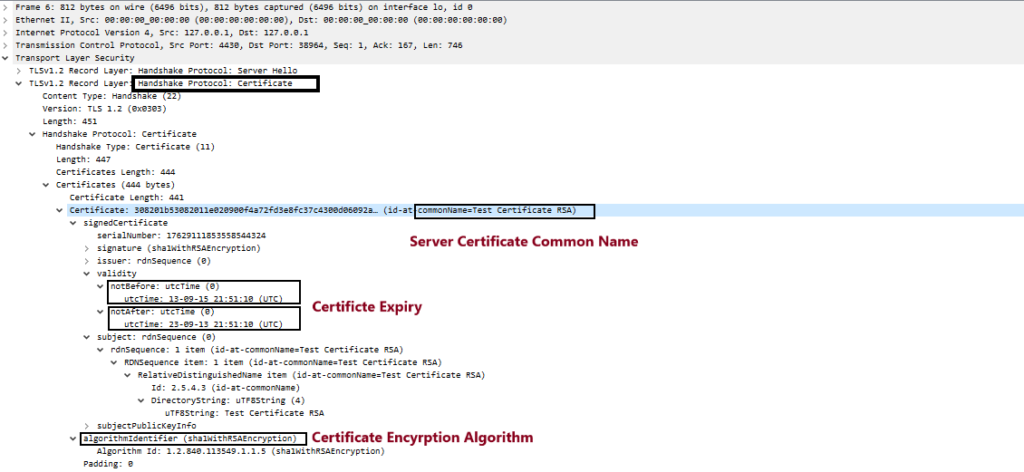
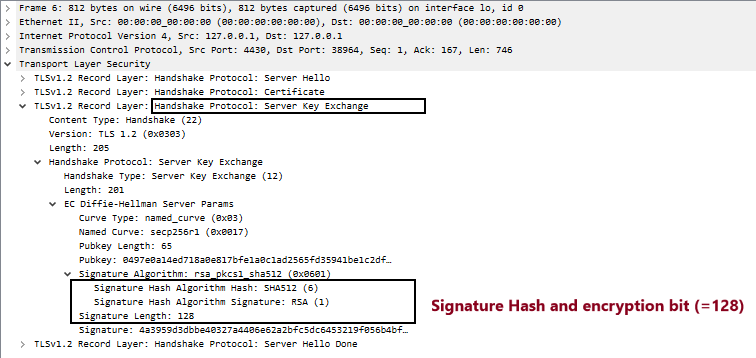
Step5. Server acknowledge with ACK, and sends back a “Server Hello”, “Server Certificate” and the “Server Key Exchange” algorithm. Look at the below screenshots explaining each of them.
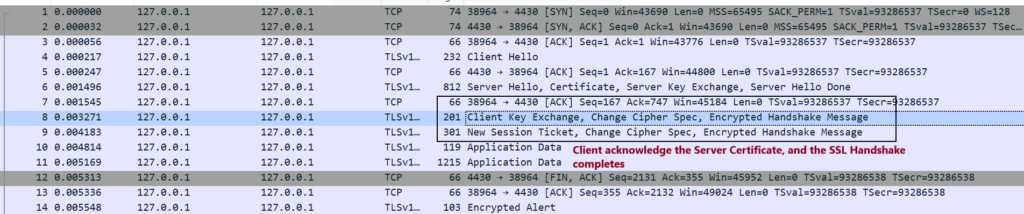
Step6. Client acknowledge the Server Certificate with ACK, and the SSL Handshake happens successfully.
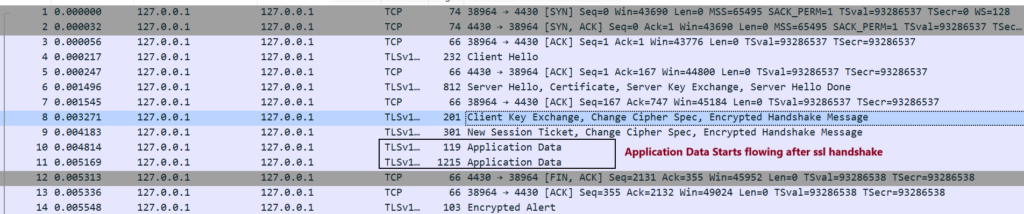
Step7. Appliction Data starts flowing after the SSL Handshake.
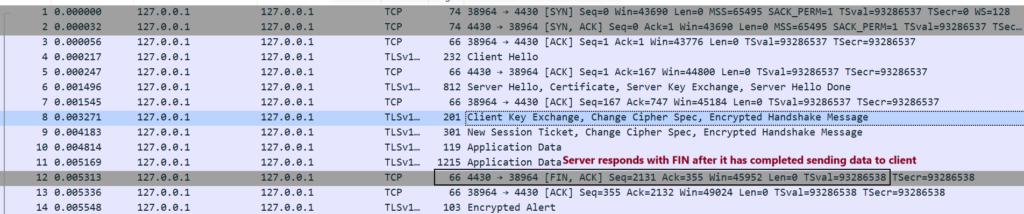
Step8. Once, server finishes sending the data for that particular request, it sends a FIN packet.
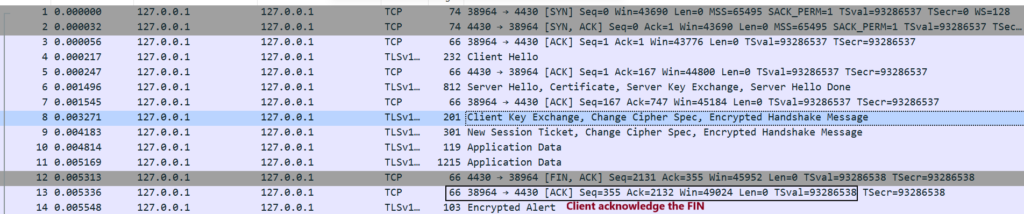
Step9. Client acknowledge the FIN packet with an ACK.
Step10. Server sends a RST packet to close the connection.