Deploy WordPress for AWS website hosting
I assume that you already have an AWS account, and know how to create a server (EC2 instance) in AWS. However, if not aware, I would recommend going to this link that has step by step details.
Save a lot of dollars configuring WordPress in AWS Cloud, instead of other standard hosting solutions e.g. Bluehost, HostGator etc. So, follow below steps to install and configure WordPress from scratch.
1. Install wget
yum install wget
2. Install MySQL
2a. Download & Update the RPM package for community Edition in RHEL 8 [We select RHEL8, since the EC2 instance installed is the same version]
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el8-1.noarch.rpm
rpm -Uvh mysql80-community-release-el8-1.noarch.rpm
2b. Disable the default mysql module
yum module disable mysql
2c. Install mysql community edition server
yum install mysql-community-server
2d. Start mysql daemon
systemctl start mysqld.service
2e. Check the RUNNING process
systemctl status mysqld.service
Refer to below output for successful startup
● mysqld.service – MySQL Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-08-04 14:42:31 UTC; 10s ago Docs: man:mysqld(8) http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/using-systemd.html Process: 15016 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/mysqld_pre_systemd (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 15089 (mysqld) Status: “Server is operational” Tasks: 39 (limit: 4936) Memory: 396.6M CGroup: /system.slice/mysqld.service └─15089 /usr/sbin/mysqld
3. Create the DB, DB User and Password
3a. Grab the temporary password created, when mysql is start at the very first time
cat /var/log/mysqld.log | grep password
2020-08-04T14:42:26.419088Z 6 [Note] [MY-010454] [Server] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: ixy__j&0qgTt
3b. Change the root password by logging in with the generated, temporary password and set a custom password for the superuser account:
mysql -uroot -p
mysql> ALTER USER ‘root’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘This1sTheNewPassword!1’;
3c. Create a Database
mysql> create database YOURDBNAME;
3d. Create a user and grant permission
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON * . * TO ‘newuser’@’localhost’;
mysql> alter user ‘newuser’@’localhost’ identified with mysql_native_password by ‘YourPassword’;
4. Install Apache WebServer
yum install httpd
5. Download WordPress
5a. Download WordPress
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
5b. Untar the files
tar -zxvf latest.tar.gz
5c. Place the exploded directory under below location
/var/www/html
6. WordPress Pre-Configuration before Install
6a. Search for the file wp-config-sample.php and copy that as wp-config.php
6b. Replace the Database name, username and password, as created earlier in wp-config.php:
define( ‘DB_NAME’, ‘database_name_here’ );
define( ‘DB_USER’, ‘username_here’ );
define( ‘DB_PASSWORD’, ‘password_here’ );
7. Start the HTTPD Service
systemctl start httpd
8. Trigger WordPress Installation
8a. Open Browser and navigate to:
http://<Your IP>/wordpress/wp-admin/install.php
8b. If you see that the webpage complains that PHP is not enabled, then goto /etc/httpd/conf.d/php.conf and make sure below lines are not commented:
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php-source
8c. Restart the httpd and refresh the browser
systemctl restart httpd
9. Go through the below screenshots for finalizing the install, after the previous step is successful
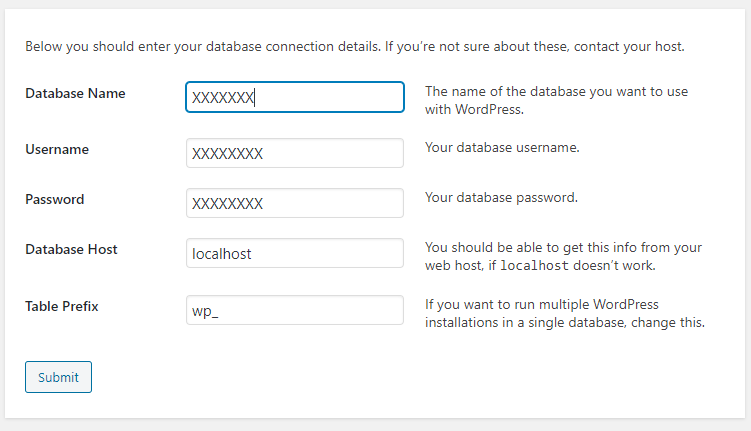
Key in the DB details configured in Step 3
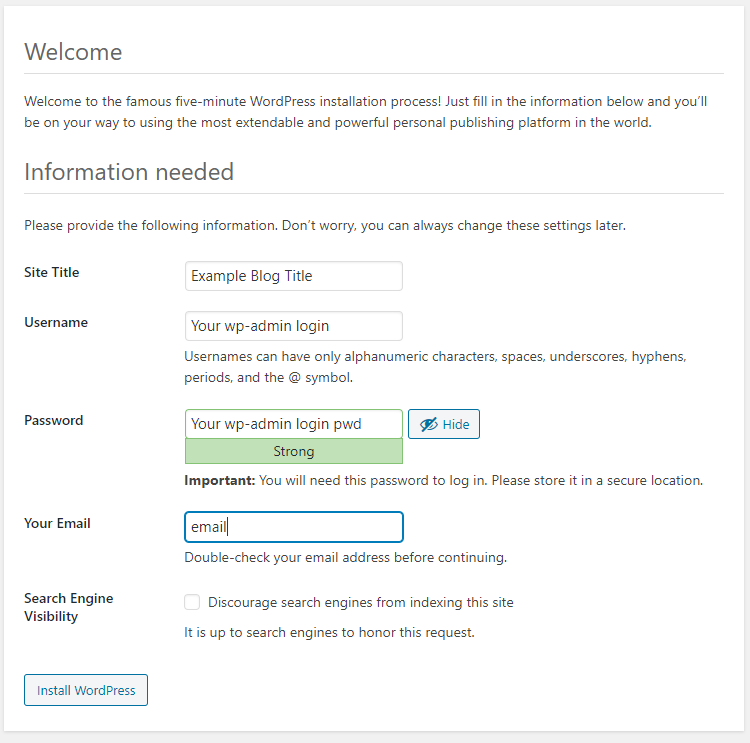
The username/password is for wp-admin login
That’s it. Once you click on Install WordPress, there will be wp-admin login prompt, and you are done with setting up wordpress base infrastructure from scratch with minimal hosting cost (As per AWS standards). Congratulations!!